Peste des petits ruminants (PPR) or sheep and goat plague is an acute viral contagious disease caused by a Morbillivirus belonging to the family of Paramyxoviridae affecting primarily sheep and goats and occasionally other species, including endangered wild populations. The disease is present in about 60% of African countries.
The World Animal Health Information System (WAHIS) is used by countries to ensure transparency in the animal disease situation worldwide, including PPR.
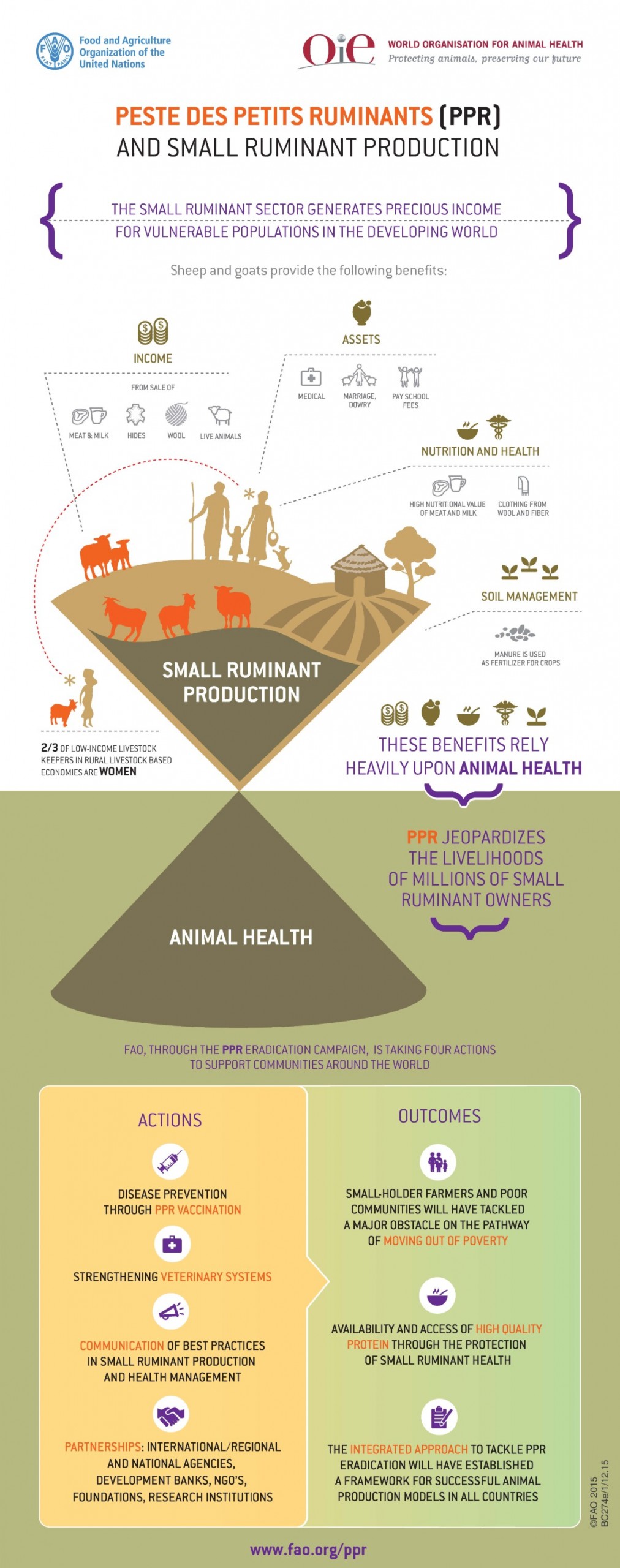
The economic impact of PPR in Africa (including production losses and costs for disease control) is estimated at about USD 147 million per year. Eradicating PPR will sustainably improve the resilience of farmers and communities and foster the economic empowerment of women in Africa which are often responsible for such small domesticated animals.
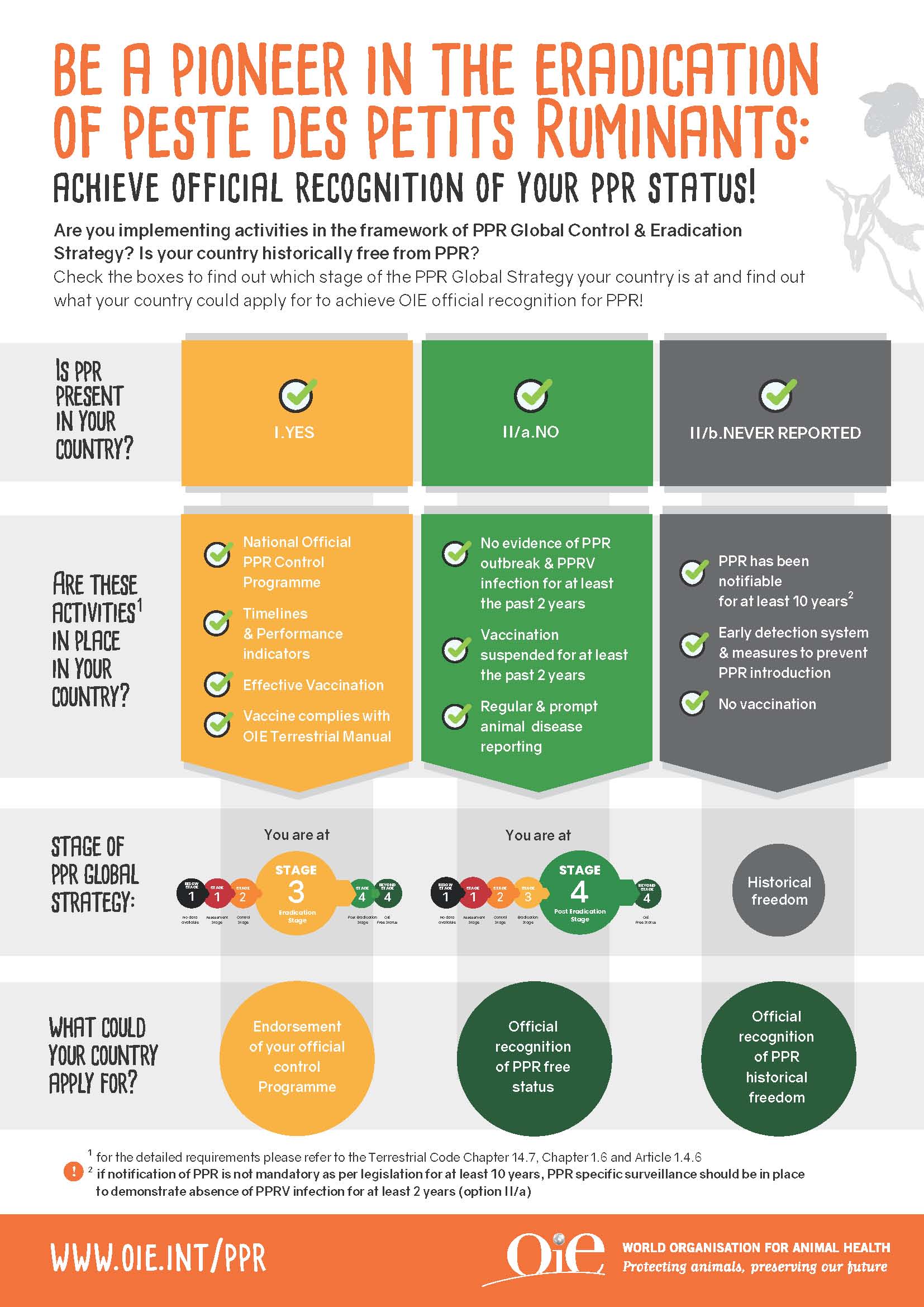
In 2015, World Organization for Animal Health -WOAH (founded as OIE) and the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO) jointly developed the PPR Global Control and Eradication Strategy, with the objective of eradicating PPR from the globe by 2030. The Strategy includes several tools and components to be implemented through a step-wise approach to decreasing levels of epidemiological risk and increasing levels of prevention and control.
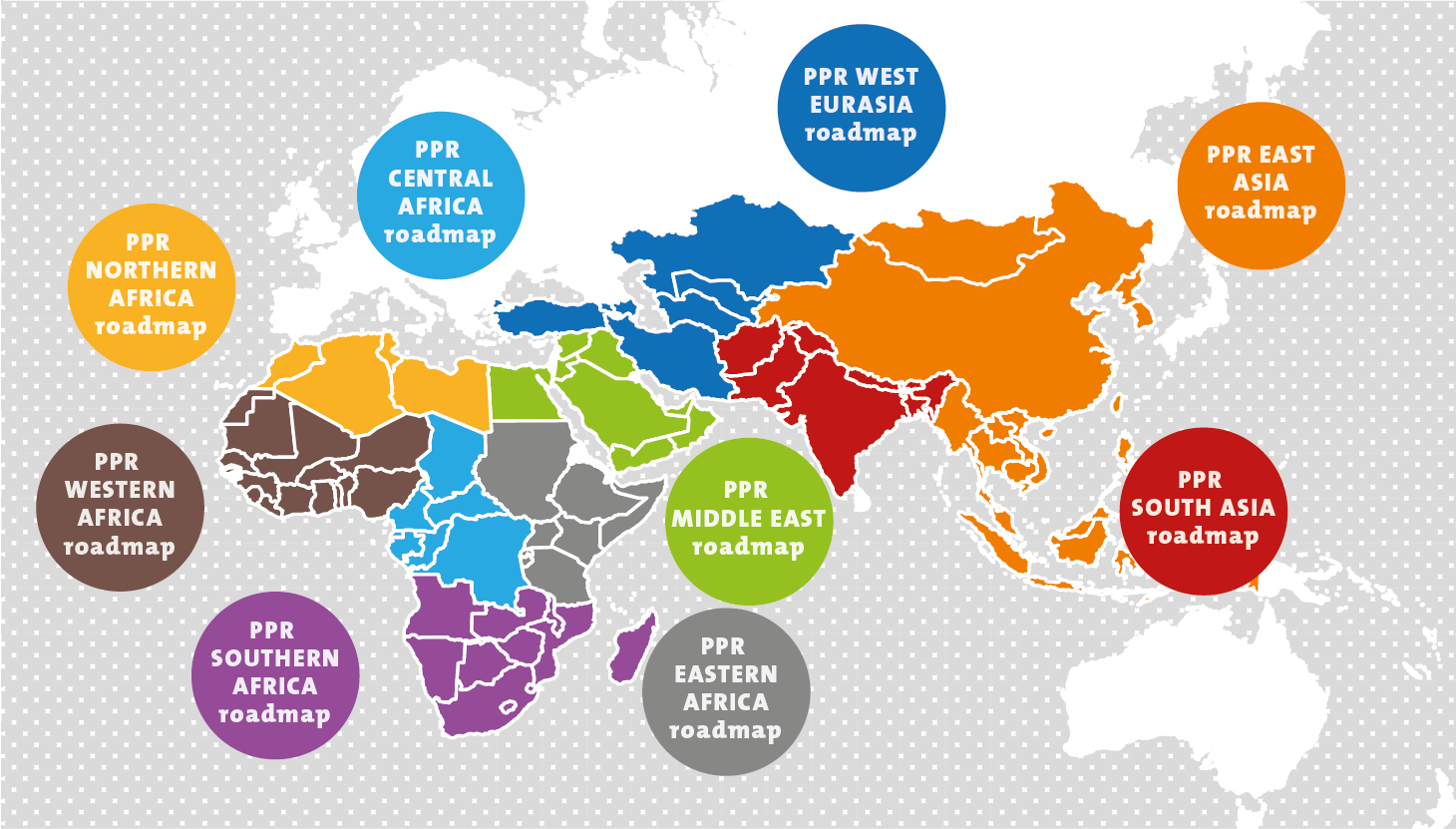
PPR Roadmaps
A joint FAO-WOAH Global Secretariat was also established in order to oversee the implementation of the Strategy. The Secretariat organises regional roadmap meetings to facilitate the elaboration and implementation of PPR regional/national action plans in line with the Global Strategy.
More information here (WOAH PPR Portal).
PPR is one of the diseases for which WOAH established a procedure for the official recognition of free disease status of Member Countries and the endorsement of an official control programme. Today, six countries in Africa are officially recognised as PPR free (country wide or zonal) :
More information here (official WOAH statuses in respect of PPR).
WOAH International Standards are available (Terrestrial Code and Manual) to guide member countries on how to improve early detection, diagnosis, surveillance, notification, vaccination programmes and better prevent the spread of the disease via international trade in animals and animal products.
Several approaches to the eradication of PPR have been piloted or supported by WOAH in recent years, i.e. the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation (BMGF) funded “Vaccine Standards and Pilot Approach (VSPA) to peste des petits ruminants (PPR) Control in Africa” which focused on Ghana and Burkina Faso as pilot countries and helped establish WOAH Regional PPR Vaccine Bank (2012 – 2014) and the ongoing World Bank funded Projet Regional d’Appui au Pastoralisme dans le Sahel (PRAPS or Regional Support to Pastoralism in the Sahel project). The project (2015 – 2021) supports PPR vaccinations in Burkina Faso, Chad, Mali, Mauritania, Niger and Senegal.
PPR
PDF - 635.34KB
PPR English
Disease outbreak maps:
http://www.oie.int/wahis_2/public/wahid.php/Diseaseinformation/Diseaseoutbreakmaps
Disease distribution maps:
http://www.oie.int/wahis_2/public/wahid.php/Diseaseinformation/Diseasedistributionmap
Latest immediate notifications to WOAH :
12/03/2025 Burkina Faso : Peste des petits ruminants
03/09/2024 Gabon: Peste des petits ruminants
02/10/2023 Rwanda : Peste des petits ruminants
22/07/2022 Algeria: Peste des petits ruminants
08/10/2021 Morocco: Peste des petits ruminants
25/03/2021 Algeria: Peste des petits ruminants
07/10/2020 Libya : Peste des petits ruminants
10/02/2020 Morocco : Peste des petits ruminants
17/04/2019 Libya : Peste des petits ruminants
20/12/2018 Algeria : Peste des petits ruminants
07/08/2018 Sierra Leone : Peste des petits ruminants
11/01/2018 Burundi : Peste des petits ruminants
15/08/2016 Tunisia : Peste des petits ruminants
12/02/2016 Algeria : Peste des petits ruminants
16/07/2015 Liberia : Peste des petits ruminants
06/07/2015 Zambia : Peste des petits ruminants
03/07/2015 Morocco : Peste des petits ruminants
FAO / OIE (WOAH) Global Strategy (2015)
Global Eradication Plan (2017 – 2021)
PDF - 834.70KB
PDF - 1.08MB